🩺 The Pulse: How to save hours on research tasks, Nvidia's healthcare strategy
November 13, 2024
1. Triage – Your Weekly Rundown
Hi Pulse Readers - this week, we’re spotlighting:
NVIDIA’s latest advancements which hint at a future with assistive robotics and AI healthcare agents.
We also take a look at new diagnostic imaging models from Microsoft,
and show you how you can supercharge your research tasks by getting practical with AI.
2. Case Study – Your Weekly Practical
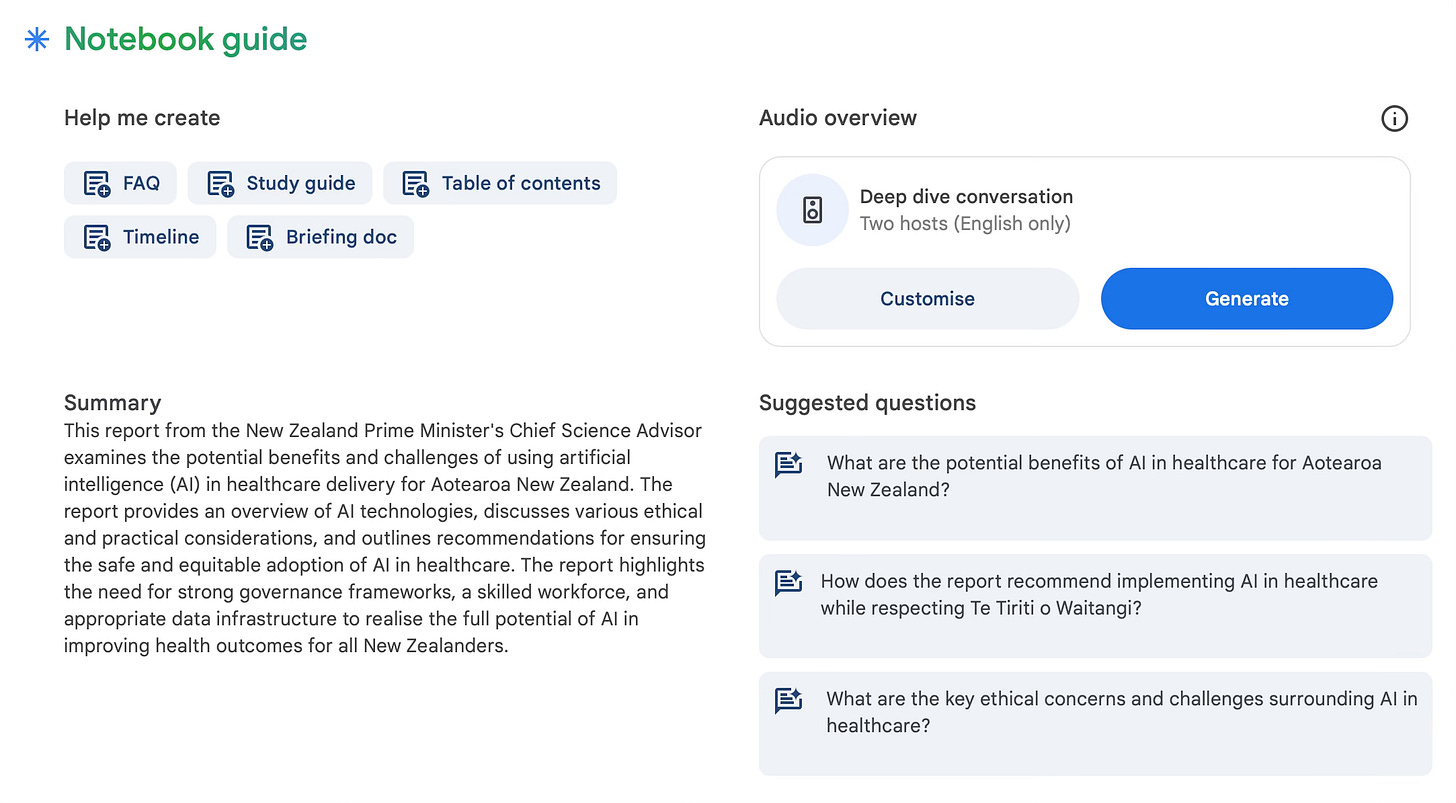
Image Source: Google NotebookML
Case Presentation: Staying updated with the latest guidelines and/or research is essential but time-consuming.
Approach: Notebook ML, a machine learning-powered notebook tool developed by Google, helps clinicians and practice managers quickly make sense of complex documents, guidelines or research - in turn saving valuable time. With a few simple steps, Notebook ML can turn dense content into concise, actionable summaries, study guides or even an engaging audio podcast.
How to Use Notebook ML for Research Summaries:
Upload or Import Text: Start by importing documents, research papers or any other web link into Notebook ML via drag-and-drop or file upload options for quick access. Don’t upload sensitive, non-public or patient-identifiable information.
Utilise the Notebook Guide: The Notebook Guide is a quick start tool that provides a variety of out-of-the box options such as generating study guides, FAQs and even audio summaries. Alternatively use the prompt window to input any specific research question you may have.
Adjust Length and Tone: Use the prompt window to customise the length and tone of the response to fit your needs (e.g., shorter summaries for quick reviews, more detailed summaries for in-depth understanding).
Review: Review the generated output as the tool can provide inaccurate information. Ensure it covers essential points accurately, then copy for easy sharing with colleagues or integration into workflows.
Outcomes: Notebook ML can save hours on research tasks, helping healthcare professionals stay current with the latest evidence and guidelines, even with limited time.
3. The Pulse - Your weekly Update
Microsoft Unveils New AI Models for Medical Imaging
Image Source: Microsoft
Microsoft’s new AI-powered medical imaging tools in Azure aim to improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. These models support multimodal analysis, meaning they can process diverse data types like CT scans, MRI images, and more, assisting radiologists in better identifying complex conditions.
Tool: Available in Microsoft’s Azure AI catalog for healthcare providers.
Functionality: Multimodal capabilities enable more comprehensive insights from medical images.
Potential Impact: Reduces diagnostic errors and accelerates image interpretation.
Implications: For clinical settings, these tools could transform how quickly and accurately clinicians diagnose conditions, especially in radiology-heavy fields.
Actionable Steps:
Explore Partnerships: Clinics and hospitals could consider partnerships with Microsoft or Microsoft partners to access these models.
Trial in Practice: Pilot these tools in departments that heavily rely on imaging, like oncology or neurology.
NVIDIA's Strategy in AI-Driven Healthcare and Robotics
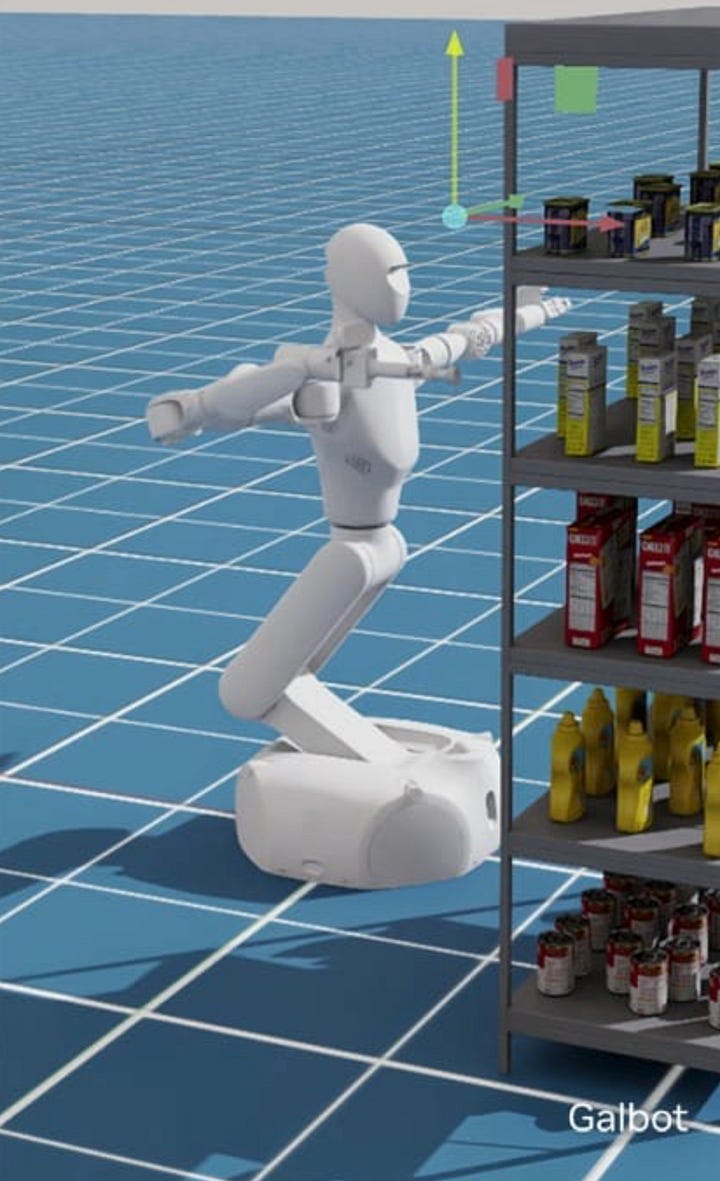

NVIDIA, known for its powerful graphics technology, is making waves in healthcare with cutting-edge AI solutions. The company is expanding beyond graphics to develop AI-driven tools like assistive robots and virtual healthcare agents, aiming to make healthcare more efficient and accessible. Their latest announcement showcases new tools for training humanoid robots, including the Isaac Lab open source robot learning framework and project GR00T.
Nvidia is not hiding it’s ambitions In the healthcare realm, embodied by NVIDIA’s partnership with Hippocratic AI, a start-up developing non-diagnostic AI healthcare agents that provide support in chronic care, remote monitoring, aged care and other patient-centric roles; but have been criticised for potentially replacing nurse tasks for $9 an hour.
Project GR00T: Focuses on providing foundational AI models for advancing robotics capabilities for lifelike interactions, potentially positioning robots as future clinical aides.
Hippocratic AI: A partnership delivering generative AI agents specialized in healthcare, prioritizing safety and utility in various non-diagnostic clinical settings.
Implications: NVIDIA’s investment in both robotics and healthcare AI suggests a future where AI and humanoid robots and virtual AI agents could support clinical staff, from patient handling to administrative assistance, helping to alleviate workforce shortages. While NVIDIA’s technology holds promise for enhancing clinical efficiency, there are potential downsides to consider:
Reliability and Safety: As humanoid robots and healthcare agents integrate more deeply into clinical workflows, issues such as data security, patient privacy, and system reliability must be addressed.
Cost and Workforce Impacts: The high costs associated with these advanced technologies may limit accessibility and divert investment away from human workers.
Impact on Patient Experience: There are fears reliance on robotic assistance and AI agents might lead to reduced human interaction, potentially impacting patient satisfaction and patient experience.
Actionable Steps:
Evaluate Potential and Risks: Healthcare leaders may consider the long-term applications of humanoid robots and virtual agents for clinic tasks.
Stay Updated: Follow NVIDIA’s updates as they refine tools aimed at healthcare.
4. Vitals – Quick Bytes
Oracle’s AI-First EHR: Oracle is developing an AI-first electronic health record (EHR) system, aiming to revolutionize data management in clinical settings by providing real-time insights, predictive analytics, and a user-friendly interface for clinicians. This development promises to enhance patient care and streamline administrative workflows. Watch the fireside chat with Oracle Founder and CTO Larry Ellison from Oracle Health Summit 2024 here.
AI Platform for Arthritis Detection Secures Funding: A UK-based AI platform designed to improve early detection of arthritis has secured a £1.2 million grant. The platform, developed by a team of researchers and clinicians, uses advanced imaging and machine learning algorithms to detect early signs of arthritis more accurately, potentially reducing the need for invasive procedures. This funding aims to expand its research and development, with hopes of improving diagnostic pathways and patient outcomes in rheumatology.
(digitalhealth.net)
We’d love to hear your thoughts, so joint the conversation by leaving a comment below:
Stay tuned for more insights in next week's edition of The Pulse.
Have a great day & see you next week!
Your Hendrix Health Team