🩺 The Pulse: China's AI Virtual Hospital
Plus: Plan your Christmas party with ChatGPT and Sora's video potential
1. Triage – Your Weekly Rundown
Ho ho ho Pulse Readers - this week, we’re highlighting:
China’s virtual hospital with self-evolving AI doctors,
how OpenAI’s Sora is opening new doors for visual patient education,
and how you can use AI to take the stress out of planning your next medical centre team event.
2. Case Study – Your Weekly Practical
Image Source: generated with Recraft.ai
Planning Your Next Event with ChatGPT
Case Presentation: Organising a festive Christmas party for your medical centre can be challenging, especially with busy schedules. Tools such as ChatGPT can help simplify the process, offering creative ideas for food, activities, and decor while considering budget and time constraints.
Approach: Use ChatGPT as your planning assistant by providing detailed prompts to generate ideas tailored to your team’s preferences and resources.
1. Define Your Theme and Vision
Prompt Example:
"I’m planning a Christmas party for our medical centre staff. We want a fun and festive theme suitable for doctors, nurses, and admin staff. Please suggest 3 creative themes with decor, outfit ideas, and activities."
2. Create a Festive Menu
Prompt Example:
"Plan a Christmas party menu for 30 people, including finger foods, a main dish, desserts, and non-alcoholic drinks. We have a mix of vegetarians and meat eaters. Include easy-to-prepare and budget-friendly options."
3. Plan Activities and Entertainment
Prompt Example:
"Suggest engaging Christmas party activities for a medical centre team. We want team-building games, a Secret Santa gift exchange, and some fun prizes. Include instructions for at least one activity."
4. Set a Budget and Shopping List
Prompt Example:
"Help me create a budget for a Christmas party for 30 people. We need decor, food, drinks, and small gifts. Break it down into categories, and provide a detailed shopping list."
We hope these tips help to get the creative juices flowing… try it for your next event!
3. The Pulse - Your weekly Update
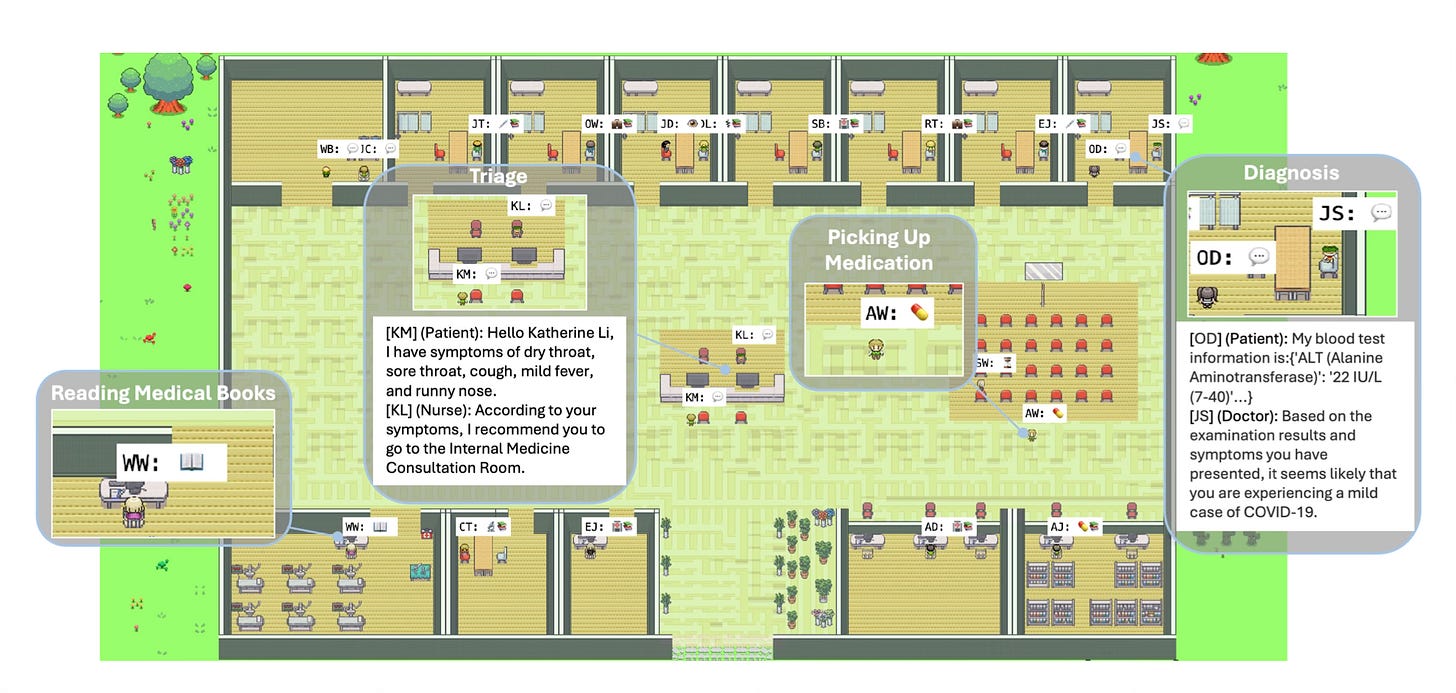
China’s Self-Evolving AI Virtual Hospital
Image Source: Tsinghua University’s Institute for AI Industry Research
Tsinghua University’s Agent Hospital, a self-evolving virtual healthcare platform, is slated for public release in 2025. Utilizing AI-generated doctors, nurses, and patients, the system simulates real-world clinical workflows, offering advancements in training of AI agents for clinical applications.
Key Features:
MedAgent-Zero Framework: Allows AI doctors to learn continuously from interactions, literature, and outcomes.
Simulated environment covers diagnostics, treatments, and follow-ups.
AI doctors achieved up to 93.06% accuracy in tasks like diagnosis of respiratory conditions
Implications:
By simulating tens of thousands of cases in days without the need for human-labeled data, the system accelerates the proficiency of AI agents to carry out clinical tasks such as triaging, diagnosing and treating patients with increasing accuracy.
While those agents could help to alleviate clinician shortages and free clinician’s time for complex tasks, it raises ethical concerns about accountability in patient care, and broader questions about the respective roles of doctors and AI agents in the future.
Still a long way to go, but definitely one to watch.
For more insights, check the full study here.
OpenAI Unveils Sora: What are the implications for healthcare?
Image Source: generated with Sora, via Sora.com
OpenAI has launched Sora, an AI model that generates videos from text prompts. This innovation shows potential to significantly enhance healthcare communication and education by enabling personalised, visual content creation.
Key Features:
Dynamic Video Creation: Sora can generate videos up to 20 seconds long based on user-provided text prompts.
Versatile Applications: Tools like "Remix," "Loop," and "Blend" allow users to customize and enhance video content.
Accessible: Available to ChatGPT Plus and Pro subscribers, Sora democratizes video production with minimal technical requirements.
Implications for Patient Care:
Sora could redefine how healthcare providers communicate with patients:
Personalised Patient Instructions: Clinicians could create tailored videos explaining post-operative care, medication usage, or chronic disease management.
Physiotherapy Demonstrations: Visual guides for physical therapy exercises could improve patient adherence and outcomes.
Health Education: Public health campaigns and condition-specific education could be delivered in engaging, accessible video formats.
Challenges and Considerations:
While promising, Sora's applications in healthcare are not without challenges:
Quality and Accuracy: Ensuring videos are clinically accurate and free from visual inconsistencies is still currently challenging, especially with the early maturity state of the technology. Also, videos cannot be generated with accompanying audio as of today.
Ethical Use: Safeguards will be critical to prevent misuse, such as generating misleading or harmful content.
Integration with Workflows: Providers will need efficient processes to incorporate text-to-video tools into clinical practices.
As Sora evolves, its potential to enhance patient education and support healthcare professionals makes it a tool worth watching in the AI healthcare landscape.
We also expect to see other solutions develop in the text-to-video space that are more suited to narrower healthcare use cases.
4. Vitals – Quick Bytes
Scientists Propose Global Collaboration on AI Virtual Cell
Researchers from Stanford, Genentech, and the Chan-Zuckerberg Initiative propose a global effort to create an AI-powered virtual human cell. This model could simulate cellular behavior, accelerate drug discovery, and advance personalised medicine. Achieving it will require massive datasets and unprecedented collaboration across disciplines. (stanford.edu)Neuralink Launches Study to Connect Brain Implants with Robotic Arms
Neuralink has announced the CONVOY study to test its N1 brain-computer interface implant for controlling assistive robotic arms. The implant interprets neural activity, enabling individuals with quadriplegia to operate devices or robotic limbs with their thoughts. This advancement marks a step toward integrating robotics with neural technology for restoring mobility and independence. (mobihealthnews.com)AI Surpasses Experts in Neuroscience Predictions
A new study shows large language models (LLMs) outperform human neuroscientists in predicting experimental outcomes, achieving 81.4% accuracy compared to 63.4% by experts. By analysing patterns in vast scientific datasets, models like BrainGPT can uncover hidden insights to guide future studies and streamline discovery processes.(nature.com)
We’d love to hear your thoughts, so joint the conversation by leaving a comment below:
We are taking a break to recharge the batteries over the holiday period and will be back with your next issue of The Pulse the week of January 6th.
Wishing you all a relaxing festive season & see you in the New Year!
Your Hendrix Health Team