🩺 The Pulse: AI Transforming Clinical Trials
Plus: the open-source imaging tool redefining diagnostics, how to create public health posters with AI
1. Triage – Your Weekly Rundown
Hi Pulse Readers - this week, we’re highlighting:
how TrialGPT is streamlining patient recruitment for clinical trials,
how a Microsoft open-source model is democratizing medical imaging analysis,
and how you can quickly create impactful public health posters with AI.
2. Case Study – Your Weekly Practical
Image Source: generated with Recraft.ai
Creating Public Health Posters with Recraft.ai
Case Presentation: Public health campaigns require engaging visuals to effectively communicate messages. Designing these posters can be time-intensive and resource-heavy.
Approach: Recraft.ai simplifies the process by using AI to create professional-grade public health posters tailored to your target audience. The platform, which recently shot to the top of the text-to-image leaderboard, provides a generous free tier and enables rapid poster creation with minimal effort.
How to Use Recraft.ai for Public Health Posters
Set Up Your Project:
Log in to Recraft.ai and select “New project” and then use the “Frame” object to select the format for your poster (1:1, 4:3, etc).Input Your Key Message:
Use the text prompt feature to describe your poster’s goal, e.g., “Create a poster encouraging flu vaccination for young adults.” You can use the text tool to add specific text you would like to include in the frame, as well as any reference images.Customize the Design:
Once generated, edit colors, fonts, and layouts to align with your branding. Add images, icons, or QR codes for additional information or links to resources.Generate Variations:
Let Recraft.ai generate multiple design options. Review and refine the one that best fits your needs. You can also choose different styles such as hand-drawn or scientific styles.Download and Share:
Export the finished poster in high resolution for printing or digital distribution.
Outcomes: Recraft.ai empowers practice managers and clinicians to create visually appealing, impactful posters quickly and cost-effectively, ensuring critical messages reach their intended audience.
3. The Pulse - Your weekly Update
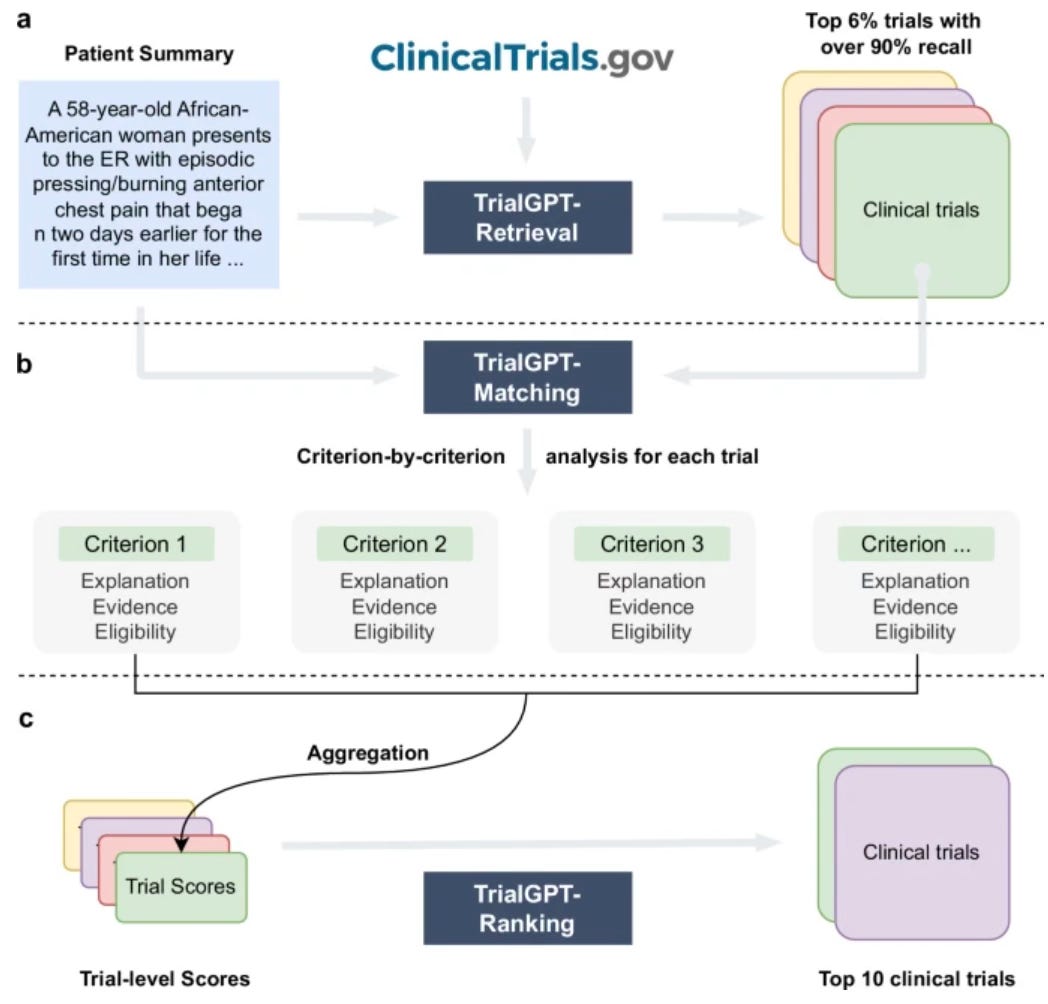
Matching Patients to Clinical Trials Using TrialGPT
Image Source: Nature Communications
Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have transformed patient recruitment for clinical trials, a traditionally labor-intensive process. Researchers have developed TrialGPT, a large language model (LLM)-driven framework that matches patients to clinical trials with remarkable efficiency and accuracy.
Key Features:
Three-Step Matching: TrialGPT employs retrieval, matching, and ranking to identify trials suited to individual patients, recalling over 90% of relevant trials with less than 6% of the initial collection analyzed.
Enhanced Accuracy: With an accuracy rate of 87.3% in predicting patient eligibility at a criterion level, TrialGPT delivers results comparable to human experts while offering detailed explanations and sentence-level evidence.
Efficiency Gains: A pilot study demonstrated a 42.6% reduction in screening time, significantly accelerating patient-trial matching processes.
Impact:
TrialGPT has the potential to revolutionise clinical trial recruitment by reducing human errors, expediting trial matches, and enabling greater scalability.
For more insights, check the full study here.
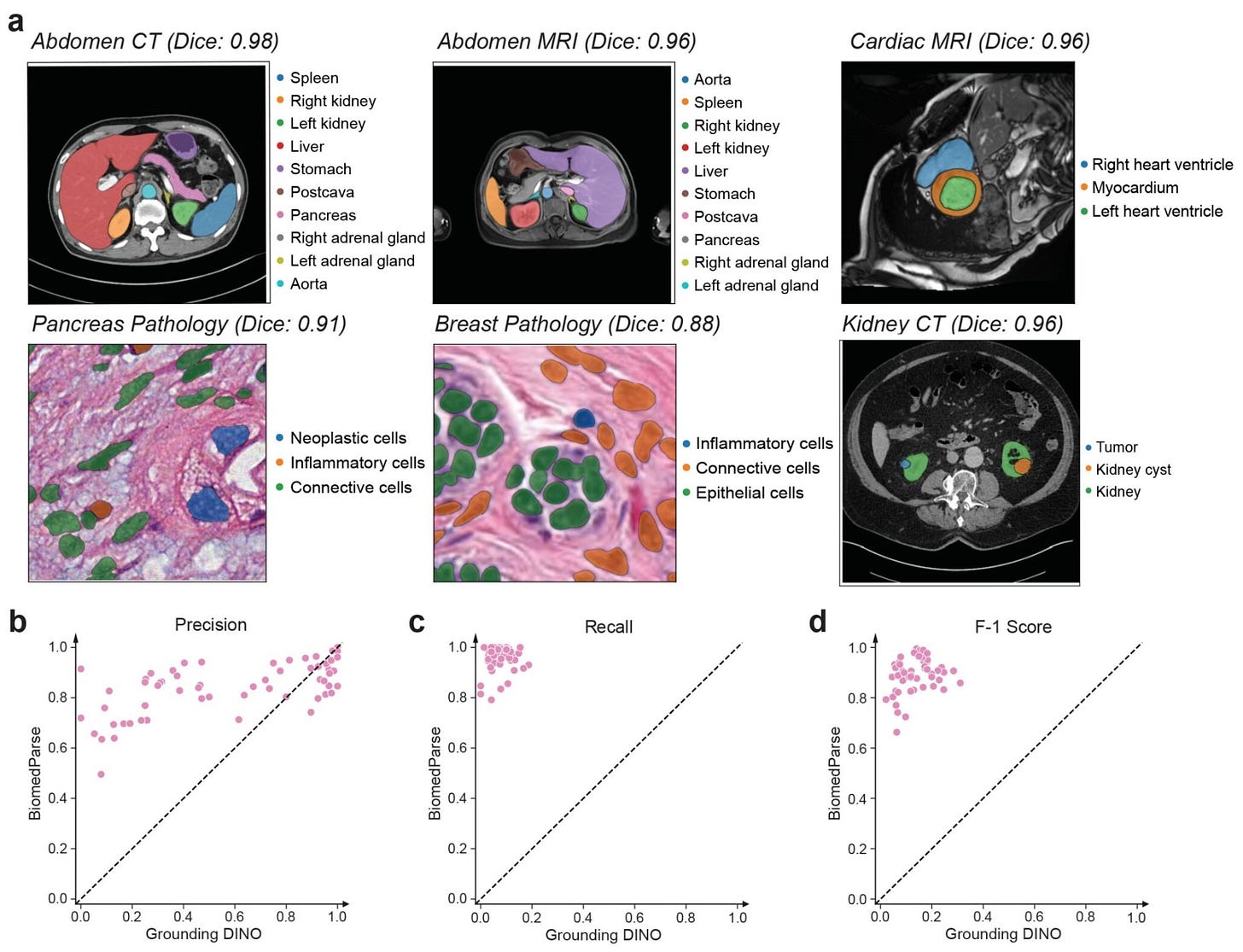
Microsoft Unveils Open-Source Model for Medical Imaging Analysis
Image Source: Microsoft
Microsoft has unveiled BiomedParse, a GPT-4-powered AI foundation model designed to transform biomedical image analysis. This new tool unifies object recognition, detection, and segmentation, enabling clinicians to analyse medical imagery - from tumors to COVID-19 infections - using simple text prompts.
Key Features:
Unified Framework: Unlike previous tools that separately perform object detection and segmentation, BiomedParse integrates these tasks for a holistic image analysis experience.
Natural Language Input: Users can specify objects for analysis using simple text prompts, eliminating the need for manual bounding boxes.
Data-Driven Precision: The model was trained on BiomedParseData, a dataset of over 6 million image-mask-description sets covering 64 object types and 82 subtypes.
Implications:
BiomedParse outperformed previous best methods like MedSAM and SAM in all evaluated metrics, particularly excelling in segmenting irregularly shaped objects, a common challenge in medical imaging. Its ability to identify and segment objects without additional user input reduces errors and increases efficiency.
Available under an Apache 2.0 license and deployable on Azure AI, BiomedParse is positioned to democratize access to advanced biomedical imaging tools.
4. Vitals – Quick Bytes
Study Highlights Bias in AI Driven by Racial Differences in Lab Testing
A recent study from the University of Michigan highlights how racial disparities in laboratory testing could introduce bias into AI models used in healthcare. The research found that African-american patients were significantly less likely than Caucasian patients to receive certain tests, such as complete blood counts or metabolic panels, during emergency department visits. This discrepancy risks skewing AI models trained on such data, potentially amplifying existing healthcare inequities. Read the study here.Hippocratic AI’s Patent Advances Safety in Healthcare LLMs
Nvidia-backed start up Hippocratic AI has patented Polaris, a safety-focused framework that combines multiple AI models to verify outputs in healthcare applications. Its architecture, involving engines for tasks like medication reconciliation and chronic care management, aims to prevent errors while assisting with pre-op, discharge, and billing processes. With accuracy exceeding 99%, Polaris reflects a growing trend in safety-driven AI in healthcare (business wire.com)AI "Virtual Sitter" for Patient Monitoring
Teladoc Health has launched Virtual Sitter, an AI-driven tool designed to detect and alert hospital staff to patient movements that may lead to falls. Using computer vision, the system monitors movements, identifies risky actions, and notifies remote staff for intervention. This system aims to improve patient safety and optimize staff resources in inpatient settings. (fiercehealthcare.com)
We’d love to hear your thoughts, so joint the conversation by leaving a comment below:
PS: Thanks for your patience, we had a family emergency last week that prevented us from publishing our weekly newsletter, back to our usual weekly schedule now.
Have a great day & see you next week!
Your Hendrix Health Team