🩺 The Pulse: AI cameras preventing medication errors, Robots learn surgeries from studying video
Issue 3 - 20 Nov 2024
1. Triage – Your Weekly Rundown
Hi Pulse Readers - this week, we’re diving into:
wearable AI cameras that can help to prevent medication errors,
DaVinci robots mastering surgical skills through video training,
and we explore practical ways to use AI tools like ChatGPT for mind-mapping, empowering clinicians to explore and dive deeper into complex topics.
2. Case Study – Your Weekly Practical
Image Source: ChatGPT.com
Case Presentation: A mind map can be useful tool to get a quick overview of a topic area, and provides a good starting point to identify specific areas of study interest. It can also be helpful as a starting point for planning training sessions for RMOs and other team members.
Approach: Large Language Models (LLMs) can be used to quickly familiarize yourself with concepts that you want to learn more about.
How to Use LLMs for Mind Mapping:
Browse to an LLM tool: such as ChatGPT, Perplexity (no sign in required) or Claude (requires sign in) and find the prompt window to start creating your mind-mapping prompt.
Begin your prompt with a role: e.g. “Act as an experienced medical educator in <country> “, or “Act as a master builder with specific experience in home renovations and <country> building regulations” are just some of the options.
Define the topic: Include “Create a mind map for <topic>” in your prompt.
Format the output: Useful additions to your prompt include “list all the main branches and sub-branches”, “add a short description”, “use a numbered list format”, “output as a table”, and so on.
Review: Review the generated output, as LLM tools can provide inaccurate information.
Diver Deeper: Once happy, you can dive deeper into any areas of interest by writing another prompt such as “I have X hours a week to study. Create a lesson plan for a X week course to help me understand <all concepts/a specific concept> and include links to specific <videos/ journal articles> that help illustrate the concept”; or “Create an outline for a 5 minute refresher training plan for a resident medical officer”; or any other question you may have.
Outcomes: Using LLMs, we can quickly familiarize ourselves with an area of interest. Try it today and let us know your results in the comments below.
3. The Pulse - Your weekly Update
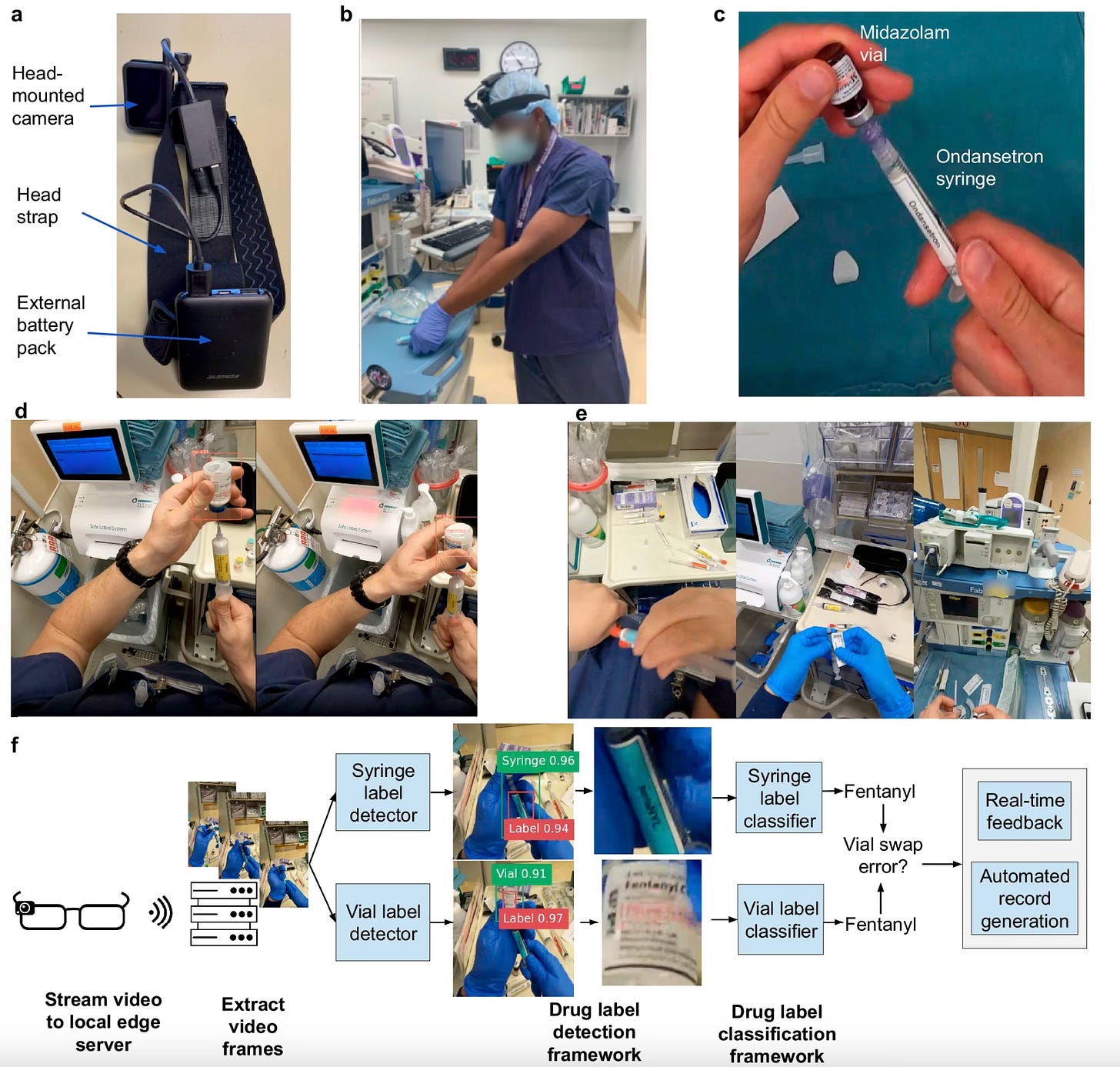
AI Wearable Cameras Prevent Medication Errors
Image Source: NPJ Digital Magazine via nature.com
A groundbreaking study published in npj Digital Medicine highlights the potential of wearable AI-powered camera systems to prevent medication errors. Developed using head-mounted cameras worn by anesthesiologists, this system employs deep learning to detect and classify drug labels on syringes and vials in real time, identifying vial-swap errors before medications reach patients.
How It Works: The camera captures drug preparation events, streams video to an edge server, and uses AI to compare syringe and vial labels for mismatches.
Performance: In trials across 17 operating rooms, the system achieved 99.6% sensitivity and 98.8% specificity in detecting errors, showcasing its potential to act as a secondary safety measure.
Applications: Designed primarily for anesthesiology, this technology could be adapted for broader use in emergency departments, ICUs, and routine care settings to reduce preventable drug-related harm.
Implications: This technology showcases potential to be a significant step in reducing medication errors, with currently up to 12% of these errors resulting in serious harm or death1. Estimate range from 140,000 up to 440,000 deaths annually in the United States are due to medical errors2,3,4, with 41% of adverse events occurring in the operating room.
There are still challenges to overcome until this technology is widely deployed to save lives however - clinician acceptance being the major factor - which could be addressed through tighter workflow integration and overcoming hardware limitations (e.g., battery life, weight/size and connectivity).
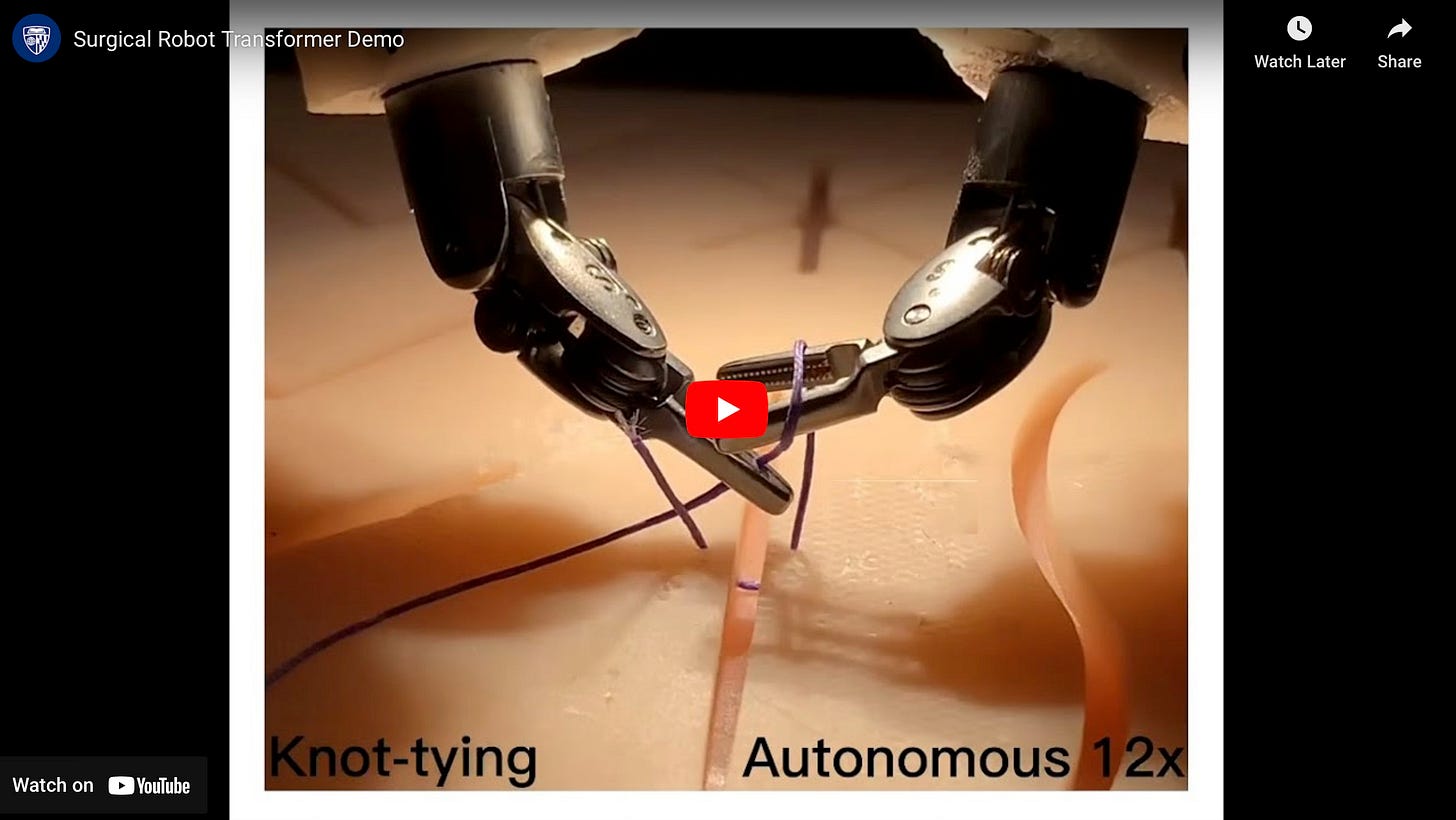
Robots Trained with Surgery Videos Achieve Human-Level Skill
Researchers at Johns Hopkins University have developed a breakthrough system using imitation learning to train surgical robots by analyzing videos of skilled surgeons using the DaVinci system. This method eliminates the need for painstakingly coding every robotic movement and opens the door to fully autonomous surgical procedures.
How It Works: The system uses video data captured by cameras on da Vinci surgical robots, training models to predict robotic movements based on visual input and relative motion rather than absolute commands.
The AI Edge: Similar to the architecture behind ChatGPT, the model translates video into robotic actions, enabling it to adapt in real-time and even recover from errors, such as dropped needles.
Implications: This advancement could shorten training times for new robotic procedures, reduce medical errors, and provide precise surgical care in remote or underserved areas.
We’ll keep you updated on regulatory and clinical trials involving this technology. Safety validation, surgeon acceptance, and integration into diverse clinical workflows will be key hurdles.
4. Vitals – Quick Bytes
Google Open-Sources AlphaFold 3: Google DeepMind has open-sourced AlphaFold 3, the latest iteration of its groundbreaking AI model for protein structure prediction. This version boasts faster computations and enhanced accuracy, making it a powerful tool for researchers worldwide to accelerate drug discovery, understand diseases, and innovate in biotech. By open-sourcing the tool, Google aims to democratize access and foster collaboration in solving complex biological challenges.
(GitHub)Contactless Health Screening: An AI-powered tool presented by a team of Japanese researches offers no-contact blood pressure and diabetes screening using analysis of high speed video only.
(American Heart Association)AI Predicts Cancer Gene Activity from Biopsies: Stanford researchers have unveiled SEQUOIA, an AI program that analyzes tumor biopsy images to predict gene activity without costly genetic sequencing. This breakthrough could accelerate clinical decision-making and reduce costs in cancer care.
(Stanford Medicine)
We’d love to hear your thoughts, so joint the conversation by leaving a comment below:
Stay tuned for more insights in next week's edition of The Pulse.
Have a great day & see you next week!
Your Hendrix Health Team